|
Lesson 1 Geography of Greece |
|
|
A Mountainous Region Ancient Greeks lived in southeastern Europe and on more than 400 neighboring islands located in the Aegean and Mediterranean Seas. The largest of these islands is Crete. Most of Greece consists of rugged mountains and hills, which cover about 90 percent of the land, making the land difficult to use as farmland. Some of its best farmlands are on the Attica peninsula, which also has excellent harbors. The southern tip of the Greek mainland is a large peninsula called the Peloponnesus. |
|
|
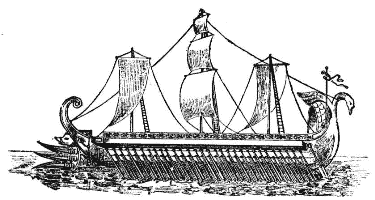
Economy of Ancient Greece Ancient Greeks raised crops such as barley, wheat, grapes, and olives. They also raised animals suited to dry, rugged land like sheep, goats, and cattle. Greek sailors traveled the Mediterranean Sea to trade for grain with countries like Egypt. The most valuable of Greek exports was and still is olive oil. |
|
|
People of the Sea About 100 years ago, archaeologists uncovered an unknown civilization on Crete. They named it Minoa after Minos, the king of Crete. From ruins and artifacts, they concluded that Minoa was a wealthy trading culture. The Minoans exported pottery, metalwork, wine, and olive oil, too. The Phoenicians developed the alphabet that is the basis of the one we used today. |
|